Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Understanding and Managing
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects people with ovaries, often causing a range of symptoms and challenges. Understanding the condition and learning how to manage it is crucial for those who are diagnosed. In this article, we’ll delve into the clinical aspects of PCOS, from its causes and symptoms to diagnosis and management.
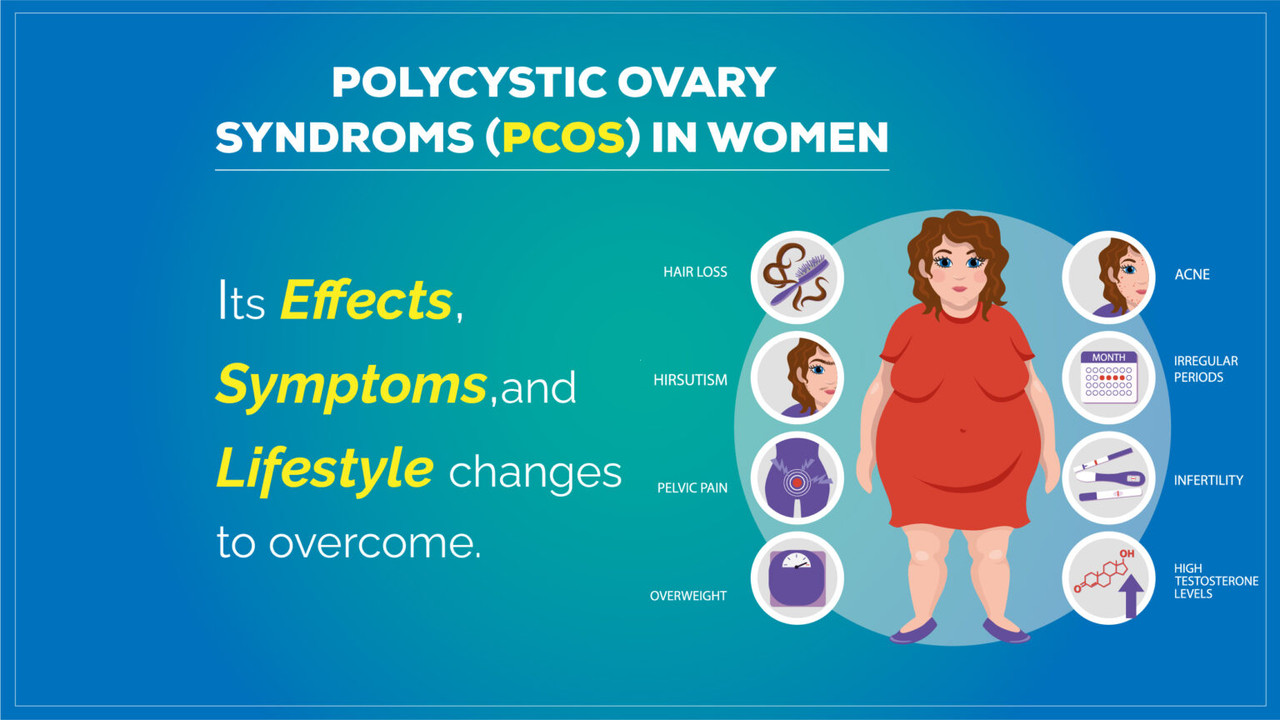
2. Common Symptoms
PCOS manifests through a range of symptoms that can affect daily life and overall health.
2.1 Menstrual Irregularities
Irregular or absent periods are common, making it difficult for those with PCOS to predict when their next period will occur.
2.2 Excess Hair Growth
Increased androgens may lead to hirsutism, causing excess hair growth on the face, chest, and back.
2.3 Acne and Oily Skin
Androgens can also contribute to acne and oily skin.
2.4 Weight Gain
Many individuals with PCOS struggle with weight management, which can worsen other symptoms.
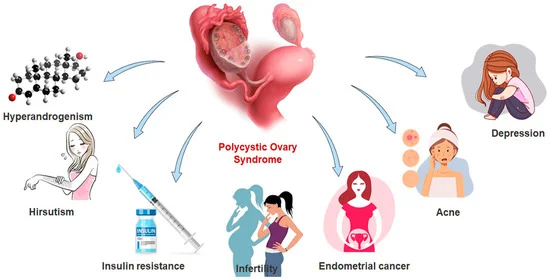
3. Potential Health Risks
PCOS is not just about troublesome symptoms; it can also lead to significant health risks.
3.1 Diabetes and Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance often goes hand in hand with PCOS, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
3.2 Cardiovascular Complications
PCOS is associated with a higher risk of heart disease and high blood pressure.
3.3 Fertility Challenges
Many individuals with PCOS experience difficulties conceiving due to irregular ovulation.
